Super shader: Difference between revisions
(→2. Detail map: added detail map information) |
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "{{Feature|Warning|" to "{{Feature|warning|") |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{TOC|side}} | ||
===Motivation, goal=== | === Motivation, goal === | ||
Super shader is a shader, which contains all standard shader techniques, such as normal, specular, ambient, detail maps and so on. Furthermore it has on input fresnel map defining course of specularity similarly to shader Glass. | |||
Super shader is shader which contains all | The goal is it to use this shader for all default in-game objects. For such objects which have not defined some maps may be used default, procedurally generated textures. | ||
=== Definition of individual stages in material === | |||
In frames are quoted default values in case we want that stage ignored. | In frames are quoted default values in case we want that stage ignored. | ||
====1. Normal map==== | ==== 1. Normal map ==== | ||
Normal map of type _NO or _NOHQ. | |||
Normal mapping is a technique used to fake the lighting of surface bumps and dents. It is used to enhance the appearance of low polygon models. The R,G,B values for each pixel in the map correspond to the X,Y,Z angle of a surface normal at that pixel. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,1,1)";</syntaxhighlight> | |||
====2. Detail map==== | ==== 2. Detail map ==== | ||
Detail map of type _DT. | Detail map of type _DT. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 20: | ||
Detail maps add to diffusion map inside one stage another repeating texture to reach greater fineness for close view onto big surfaces which would too complicated to cover with oversized texture resolution. | Detail maps add to diffusion map inside one stage another repeating texture to reach greater fineness for close view onto big surfaces which would too complicated to cover with oversized texture resolution. | ||
{{Feature|warning|DetailTexture (_DT) has painting saved inside alpha-channel (RGB components are ignored while this texture is converted from TGA to PAA). Because shader in a way multiplying detail texture with colored diffusion component, it is necessary that average color of detail texture should be 50% grey. Otherwise if material with detail texture is cutoff inside lower LOD then it may result into visible change of texture brightness (MipMapping is applied with distance and angle).}} | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0)";</syntaxhighlight> | |||
====3. Macro map==== | ==== 3. Macro map ==== | ||
Macro map _MC. | |||
Macro | Macro texture contains alternative data to basic texture. Representation of basic texture and macro texture for given place is selected by macrotexture alpha channel (1 means only macro texture , 0 means only basic texture). RGB is calculated as LERP with basic map. Detail map is applied on the end (last) thus overlay original and macro map. | ||
== | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0)";</syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== 4. AmbientShadow map ==== | |||
Ambient shadow map _AS. | Ambient shadow map _AS. | ||
Ambient shadow texture contains stored information "how much ambient light is in given place'. White color means full ambient lighting. 0 means none.In fact only channel which is taken advantage of is G - it is thus important that information is correctly in him. Rest of channels doesn't matter and anything can be placed there (may be same as in G). | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,1,1,1)";</syntaxhighlight> | |||
==== | ==== 5. Specular map ==== | ||
Specular map of _SMDI type (_SM isn't supported). _SMDI maps are bit depth optimized specular maps. Each channel in the 24 bit (RGB) SMDI map has a different function. The R channel should be set to 1 for all pixels, the G channel functions as a specular map, and the B channel functions as a specular power map (also known as gloss map, where black means very rough [matte] surface and white means very smooth [shiny] surface). | |||
Fresnel function is entered as procedural texture in following form: | ==== 6. Fresnel function ==== | ||
N and K are inputs for fresnel equation that's on theirs basics and for given angle able determine how much reflects under given angle. | Fresnel function is entered as procedural texture in following form: | ||
N and K are constant for given material and are known for individual elements. | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">texture="#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(N,K)";</syntaxhighlight> | ||
N and K (where N is refractive index and K - absorption coefficient) are inputs for fresnel equation that's on theirs basics and for given angle, able determine how much reflects under given angle. | |||
N and K are constant for given material and are known for individual elements. The following table includes a list of basic materials and their settings. The table also shows the wavelengths. | |||
Visible spectrum is approx 400 nm-800 nm. | |||
{| | Values close to the middle of this spectrum are interesting. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|'''Material''' | |'''Material''' | ||
|'''wavelength''' | |'''wavelength''' | ||
| Line 126: | Line 128: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Additional source for N and K values: | |||
* http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_refractive_indices | |||
Other values must must be found empirically. | |||
The following program can be used in TexView and can help you to find additional values. It visualizes the course of the fresnel function for given N and K values. | |||
(on left is normal line to line of sight, on right directly against line of sight, the more is value closer 1 the higher reflection is): | |||
<code style="display: block">N = 0.969770; | |||
K = 0.0118000; | |||
X = u * 0.5 + 0.5; | |||
S = acos(X); | |||
AA = sqrt((sqrt((N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2)^2 + 4*N^2*K^2)+(N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2))/2); | |||
BB = sqrt((sqrt((N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2)^2 + 4*N^2*K^2)-(N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2))/2); | |||
FS = (AA^2+BB^2-2*AA*cos(S) + cos(S)^2)/(AA^2+BB^2+2*AA*cos(S) + cos(S)^2); | |||
FP = FS*(AA^2+BB^2-2*AA*sin(S)*tan(S)+sin(S)^2*tan(S)^2)/(AA^2+BB^2+2*AA*sin(S)*tan(S)+sin(S)^2*tan(S)^2); | |||
r=1; | |||
g=1; | |||
b=1; | |||
a=(FS+FP)/2;</code> | |||
=== | ==== 7. Environmental map ==== | ||
This technology allows to show environmental reflections on materials. The reflected environment is static and only changes its lighting accordingly to time of day. Environment is characterized by the texture which is called environmental map. In our case environmental map presents hemisphere projection into plane. | |||
=== Example === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">ambient[]={1,1,1,1}; | |||
diffuse[]={1,1,1,1}; | |||
forcedDiffuse[]={0,0,0,0}; | |||
emmisive[]={0,0,0,1}; | |||
specular[]={0.7,0.7,0.7,1}; | |||
specularPower=180; | |||
PixelShaderID="Super"; | |||
VertexShaderID="Super"; | |||
class Stage1 | |||
{ | |||
texture="ca\weapons\data\aimpoint_NOHQ.paa"; | |||
uvSource="tex"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage2 | |||
{ | |||
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0)"; | |||
uvSource="tex"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage3 | |||
{ | |||
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0)"; | |||
uvSource="tex"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage4 | |||
{ | |||
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,1,1,1)"; | |||
uvSource="tex"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage5 | |||
{ | |||
texture="ca\weapons\data\aimpoint_SMDI.paa"; | |||
uvSource="tex"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage6 | |||
{ | |||
texture="#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(1.3,7)"; | |||
uvSource="none"; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage7 | |||
{ | |||
texture="ca\air\data\env_co.paa"; | |||
uvSource="none"; | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Default Values == | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="cpp">ambient[] = {1,1,1,1}; | |||
diffuse[] = {1,1,1,1}; | |||
forcedDiffuse[] = {0,0,0,1}; | |||
emmisive[] = {0,0,0,0}; | |||
specular[] = {1,1,1,1}; | |||
specularPower = 30; | |||
PixelShaderID = "Super"; | |||
VertexShaderID = "Super"; | |||
class Stage1 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,1,1,NOHQ)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage2 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,DT)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage3 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0,MC)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage4 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(1,1,1,1,AS)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage5 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(1,0,1,0,SMDI)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage6 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(0.4,0.2)"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class Stage7 | |||
{ | |||
texture = "a3\data_f\env_land_co.paa"; | |||
useWorldEnvMap = "true"; | |||
uvSource = "tex"; | |||
class uvTransform | |||
{ | |||
aside[] = {1,0,0}; | |||
up[] = {0,1,0}; | |||
dir[] = {0,0,1}; | |||
pos[] = {0,0,0}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
class StageTI | |||
{ | |||
texture = "a3\data_f\default_vehicle_ti_ca.paa"; | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Super shader inside CgFX for Autodesk Maya === | === Super shader inside CgFX for Autodesk Maya === | ||
| Line 203: | Line 301: | ||
==== Shader usage ==== | ==== Shader usage ==== | ||
In software Maya use shader as material type "Cgfx Shader". | In software Maya use shader as material type "Cgfx Shader". | ||
Then is required set path to file "Super_01.cgfx" in parameter "CgFX File" in group "CgFX Shader". | Then is required set path to file "Super_01.cgfx" in parameter "CgFX File" in group "CgFX Shader". | ||
In same directory with file "Super_01.cgfx" must be also header file "headMAYA.fxh". | In same directory with file "Super_01.cgfx" must be also header file "headMAYA.fxh". | ||
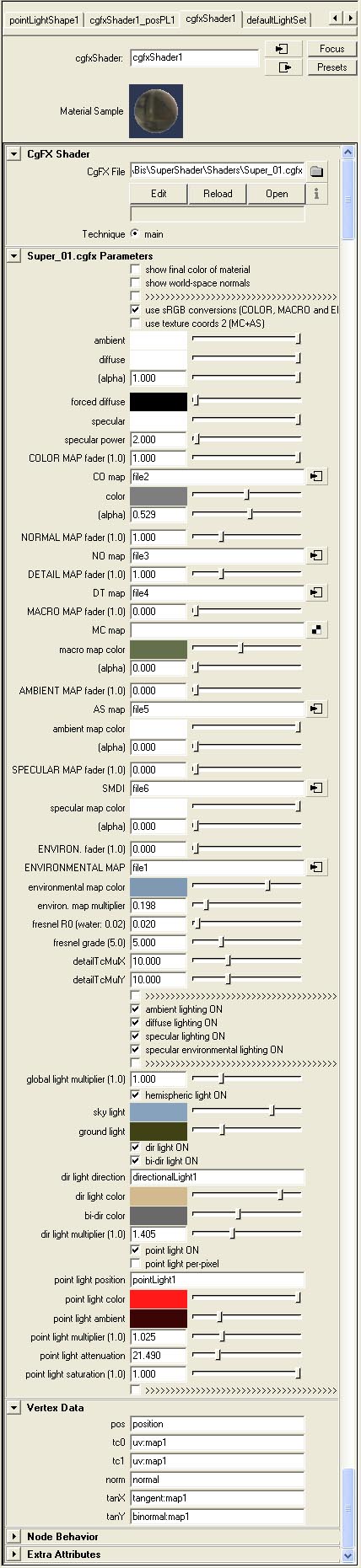
After loading cgfx file appears material | After loading cgfx file appears material parameters in options group "Super_01.cgfx Parameters" (see appended picture). | ||
==== Vertex Data ==== | ==== Vertex Data ==== | ||
| Line 227: | Line 321: | ||
'''tanX, tanY''' - tangent-space for first "wrap" (for example of settings see interface picture below) | '''tanX, tanY''' - tangent-space for first "wrap" (for example of settings see interface picture below) | ||
==== Material parameters (Super_01.cgfx Parameters) ==== | |||
==== Material | |||
| Line 246: | Line 338: | ||
'''ambient, diffuse, forced diffuse, specular''' - colors of material components; they have same meaning as in material editor Objektiv2 | '''ambient, diffuse, forced diffuse, specular''' - colors of material components; they have same meaning as in material editor Objektiv2 | ||
'''specular power''' - specular | '''specular power''' - specular strength | ||
'''TEXTURES''' | '''TEXTURES''' | ||
| Line 256: | Line 346: | ||
For each texture there is parameter '''fader''' which blends between'''substitute color''' and '''texture'''. | For each texture there is parameter '''fader''' which blends between'''substitute color''' and '''texture'''. | ||
This solution replaces procedural textures. Fader setting to 0 means that it will use only substitute color while setting mean it will use only texture. | This solution replaces procedural textures. Fader setting to 0 means that it will use only substitute color while setting mean it will use only texture. | ||
For NORMAL map there is no substitute color setup as it | For NORMAL map there is no substitute color setup as it is hardset to RGB=(0.5, 0.5, 1.0), which is default normal line direction (upright to surface). | ||
With fader it | With fader it is possible test various "strength" of normal map (values higher than 1 increasing influence while smaller decreasing influence) and then eventually alter texture. | ||
For DETAIL map the situation is similar, substitute color is hardset to RGB=(0.5, 0.5, 1.0) and you can define by fader different | For DETAIL map the situation is similar, substitute color is hardset to RGB=(0.5, 0.5, 1.0) and you can define by fader different strength. | ||
Example setting up procedural color map "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,1,CO)": | Example setting up procedural color map "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,1,CO)": | ||
| Line 269: | Line 359: | ||
'''FRESNEL''' | '''FRESNEL''' | ||
Fresnel calculation with help of coefficients N and K is not suitable for intgration into CgFX shaderu therefore it | Fresnel calculation with help of coefficients N and K is not suitable for intgration into CgFX shaderu therefore it is replaced by simpler variants which fails to naturally represent curve for metal materials. | ||
'''fresnel R0''' - specular | '''fresnel R0''' - specular strength on surface upright to direction of sight | ||
'''fresnel grade''' - curve "steepness" | '''fresnel grade''' - curve "steepness" | ||
| Line 315: | Line 405: | ||
'''point light ON''' - light switch | '''point light ON''' - light switch | ||
'''point light per-pixel''' - enable more precise lighting calculation (for testing only; it | '''point light per-pixel''' - enable more precise lighting calculation (for testing only; it is not part of super shader) | ||
'''point light position''' - link up point light in scene (right mouse button click and choose correct light) | '''point light position''' - link up point light in scene (right mouse button click and choose correct light) | ||
| Line 329: | Line 419: | ||
<BR>''Picture with interface of super-shader material inside Maya:''<BR> | <BR>''Picture with interface of super-shader material inside Maya:''<BR> | ||
[[ | [[File:SuperShaderMaya1.jpg]]<BR> | ||
| Line 343: | Line 433: | ||
To create new material dot his: Within Material editor choose free slot and set material type to "DirectX 9 Shader" (instead default "Standard"). | To create new material dot his: Within Material editor choose free slot and set material type to "DirectX 9 Shader" (instead default "Standard"). | ||
Then is needed set path to file "SuperShader.fx" inside tab "DirectX 9 Shader". | Then is needed set path to file "SuperShader.fx" inside tab "DirectX 9 Shader". | ||
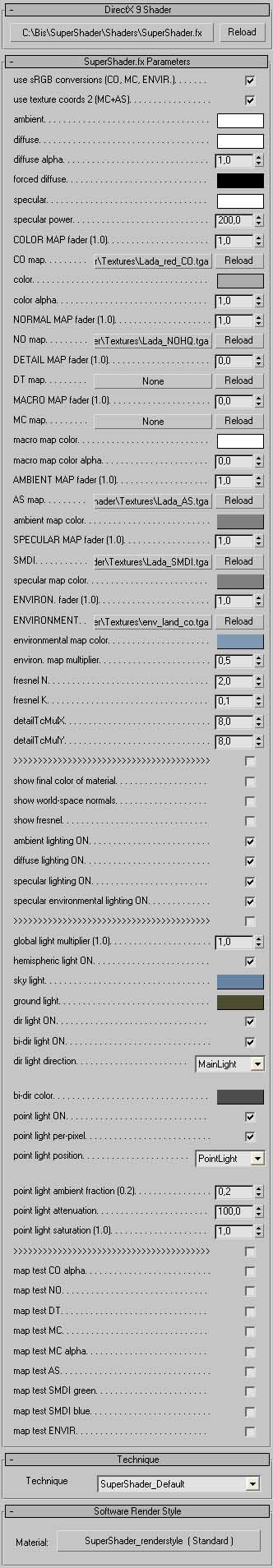
When file is loaded it will show material | When file is loaded it will show material parameters within tab "SuperShader.fx Parameters" (see appended picture). | ||
<BR>''Picture with interface of super-shader material inside 3DS Max:''<BR> | <BR>''Picture with interface of super-shader material inside 3DS Max:''<BR> | ||
[[ | [[File:SuperShaderFX01.jpg]]<BR> | ||
==== "Technique" ==== | ==== "Technique" ==== | ||
Each fx-file may include multiple techniques. For alpha blending i use standalone technique because it | Each fx-file may include multiple techniques. For alpha blending i use standalone technique because it is not possible do with just checkbox field. | ||
'''SuperShader_Default''' - for opacity geometry | '''SuperShader_Default''' - for opacity geometry | ||
| Line 356: | Line 446: | ||
'''SuperShader_AlphaBlend''' - for transparent geometry; often hard to sort and nothing can be done about it | '''SuperShader_AlphaBlend''' - for transparent geometry; often hard to sort and nothing can be done about it | ||
'''SuperShader_MapTest''' - with help of | '''SuperShader_MapTest''' - with help of parameters "map test CO alpha" till "map test ENVIR" shows on model particular texture or it is component | ||
(it's used only downmost checked option - doesn't go other way at present time; options "map test" works only in this technique | (it's used only downmost checked option - doesn't go other way at present time; options "map test" works only in this technique | ||
==== Illumination model ==== | ==== Illumination model ==== | ||
Material can be assigned one directional and one point lighting ( | Material can be assigned one directional and one point lighting (parameters "dir light direction" and "point light position"). Color and intensity is taken directly from light. | ||
'''rest is nearly same as here:''' [[ | '''rest is nearly same as here:''' [[Super shader#Super shader inside CgFX for Autodesk Maya]] | ||
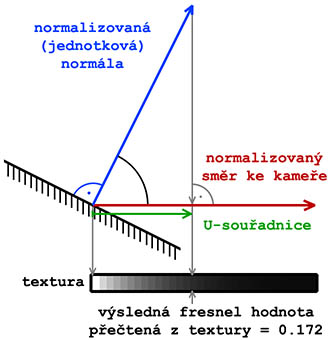
=== How is gained fresnel from procedural texture === | === How is gained fresnel from procedural texture === | ||
Procedural texture for fresnel function contains single-dimensional conversion table (visually it | Procedural texture for fresnel function contains single-dimensional conversion table (visually it is sort of brightness gradient ) from which reads value on position (U,V). | ||
Value U is calculated as scalar product between normal line and direction to the camera (both vertors must be normalized)) in each surface point of model (this value also represents cosine of angle between vectors). | Value U is calculated as scalar product between normal line and direction to the camera (both vertors must be normalized)) in each surface point of model (this value also represents cosine of angle between vectors). | ||
Value V is always 0.5, therefore it | Value V is always 0.5, therefore it is unneeded that texture height would be different than 1. | ||
For example: function with parameters N = 1.0 and K = 0.6 should be entered with width 64 and height 1: "#(ai,64,1,1)fresnel(1 | For example: function with parameters N = 1.0 and K = 0.6 should be entered with width 64 and height 1: "#(ai,64,1,1)fresnel(1,0.6)". Size of texture is then only 64 bytes instead 4096 in case if the height is 64. | ||
When we realize that such texture is generated for every material with fresnel inside scene, then saving of memory and performance is indispensable! | When we realize that such texture is generated for every material with fresnel inside scene, then saving of memory and performance is indispensable! | ||
<BR>''Picture with visual representation of obtaining fresnel value from procedural texture:''<BR> | <BR>''Picture with visual representation of obtaining fresnel value from procedural texture:''<BR> | ||
[[ | [[File:FresnelLUT.jpg]]<BR> | ||
{{GameCategory|arma2|Editing}} | |||
Latest revision as of 00:25, 2 February 2024
Motivation, goal
Super shader is a shader, which contains all standard shader techniques, such as normal, specular, ambient, detail maps and so on. Furthermore it has on input fresnel map defining course of specularity similarly to shader Glass. The goal is it to use this shader for all default in-game objects. For such objects which have not defined some maps may be used default, procedurally generated textures.
Definition of individual stages in material
In frames are quoted default values in case we want that stage ignored.
1. Normal map
Normal map of type _NO or _NOHQ. Normal mapping is a technique used to fake the lighting of surface bumps and dents. It is used to enhance the appearance of low polygon models. The R,G,B values for each pixel in the map correspond to the X,Y,Z angle of a surface normal at that pixel.
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,1,1)";
2. Detail map
Detail map of type _DT.
Detail maps add to diffusion map inside one stage another repeating texture to reach greater fineness for close view onto big surfaces which would too complicated to cover with oversized texture resolution.
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0)";
3. Macro map
Macro map _MC.
Macro texture contains alternative data to basic texture. Representation of basic texture and macro texture for given place is selected by macrotexture alpha channel (1 means only macro texture , 0 means only basic texture). RGB is calculated as LERP with basic map. Detail map is applied on the end (last) thus overlay original and macro map.
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0)";
4. AmbientShadow map
Ambient shadow map _AS.
Ambient shadow texture contains stored information "how much ambient light is in given place'. White color means full ambient lighting. 0 means none.In fact only channel which is taken advantage of is G - it is thus important that information is correctly in him. Rest of channels doesn't matter and anything can be placed there (may be same as in G).
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,1,1,1)";
5. Specular map
Specular map of _SMDI type (_SM isn't supported). _SMDI maps are bit depth optimized specular maps. Each channel in the 24 bit (RGB) SMDI map has a different function. The R channel should be set to 1 for all pixels, the G channel functions as a specular map, and the B channel functions as a specular power map (also known as gloss map, where black means very rough [matte] surface and white means very smooth [shiny] surface).
6. Fresnel function
Fresnel function is entered as procedural texture in following form:
texture="#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(N,K)";
N and K (where N is refractive index and K - absorption coefficient) are inputs for fresnel equation that's on theirs basics and for given angle, able determine how much reflects under given angle. N and K are constant for given material and are known for individual elements. The following table includes a list of basic materials and their settings. The table also shows the wavelengths. Visible spectrum is approx 400 nm-800 nm.
Values close to the middle of this spectrum are interesting.
| Material | wavelength | N | K |
| Aluminum | 600 | 1.3 | 7 |
| Cobalt | 600 | 0.2 | 3 |
| Copper | 850 | 2.08 | 7.15 |
| Gold | 600 | 0.3 | 3 |
| Iron | 886 | 3.12 | 3.87 |
| Lead | 850 | 1.44 | 4.35 |
| Molybdenum | 954 | 2.77 | 3.74 |
| Nickel | 855 | 2.59 | 4.55 |
| Palladium | 827 | 2.17 | 5.22 |
| Platinum | 827 | 2.92 | 5.07 |
| Silver | 600 | 0.2 | 3 |
| Titanium | 821 | 3.21 | 4.01 |
| Vanadium | 984 | 2.94 | 3.50 |
| Tungsten | 827 | 3.48 | 2.79 |
Additional source for N and K values:
Other values must must be found empirically. The following program can be used in TexView and can help you to find additional values. It visualizes the course of the fresnel function for given N and K values. (on left is normal line to line of sight, on right directly against line of sight, the more is value closer 1 the higher reflection is):
N = 0.969770;
K = 0.0118000;
X = u * 0.5 + 0.5;
S = acos(X);
AA = sqrt((sqrt((N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2)^2 + 4*N^2*K^2)+(N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2))/2);
BB = sqrt((sqrt((N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2)^2 + 4*N^2*K^2)-(N^2-K^2-sin(S)^2))/2);
FS = (AA^2+BB^2-2*AA*cos(S) + cos(S)^2)/(AA^2+BB^2+2*AA*cos(S) + cos(S)^2);
FP = FS*(AA^2+BB^2-2*AA*sin(S)*tan(S)+sin(S)^2*tan(S)^2)/(AA^2+BB^2+2*AA*sin(S)*tan(S)+sin(S)^2*tan(S)^2);
r=1;
g=1;
b=1;
a=(FS+FP)/2;
7. Environmental map
This technology allows to show environmental reflections on materials. The reflected environment is static and only changes its lighting accordingly to time of day. Environment is characterized by the texture which is called environmental map. In our case environmental map presents hemisphere projection into plane.
Example
ambient[]={1,1,1,1};
diffuse[]={1,1,1,1};
forcedDiffuse[]={0,0,0,0};
emmisive[]={0,0,0,1};
specular[]={0.7,0.7,0.7,1};
specularPower=180;
PixelShaderID="Super";
VertexShaderID="Super";
class Stage1
{
texture="ca\weapons\data\aimpoint_NOHQ.paa";
uvSource="tex";
};
class Stage2
{
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0)";
uvSource="tex";
};
class Stage3
{
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0)";
uvSource="tex";
};
class Stage4
{
texture="#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,1,1,1)";
uvSource="tex";
};
class Stage5
{
texture="ca\weapons\data\aimpoint_SMDI.paa";
uvSource="tex";
};
class Stage6
{
texture="#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(1.3,7)";
uvSource="none";
};
class Stage7
{
texture="ca\air\data\env_co.paa";
uvSource="none";
};
Default Values
ambient[] = {1,1,1,1};
diffuse[] = {1,1,1,1};
forcedDiffuse[] = {0,0,0,1};
emmisive[] = {0,0,0,0};
specular[] = {1,1,1,1};
specularPower = 30;
PixelShaderID = "Super";
VertexShaderID = "Super";
class Stage1
{
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,1,1,NOHQ)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage2
{
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5,DT)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage3
{
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0,0,0,0,MC)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage4
{
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(1,1,1,1,AS)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage5
{
texture = "#(argb,8,8,3)color(1,0,1,0,SMDI)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage6
{
texture = "#(ai,64,64,1)fresnel(0.4,0.2)";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class Stage7
{
texture = "a3\data_f\env_land_co.paa";
useWorldEnvMap = "true";
uvSource = "tex";
class uvTransform
{
aside[] = {1,0,0};
up[] = {0,1,0};
dir[] = {0,0,1};
pos[] = {0,0,0};
};
};
class StageTI
{
texture = "a3\data_f\default_vehicle_ti_ca.paa";
};
Super shader inside CgFX for Autodesk Maya
Shader usage
In software Maya use shader as material type "Cgfx Shader". Then is required set path to file "Super_01.cgfx" in parameter "CgFX File" in group "CgFX Shader". In same directory with file "Super_01.cgfx" must be also header file "headMAYA.fxh". After loading cgfx file appears material parameters in options group "Super_01.cgfx Parameters" (see appended picture).
Vertex Data
For correct function of material is needed rightly set "Vertex Data" for particular model.
pos - vertex position
tc0 - texture coordinates for first "wrap" (for textures CO, NO, DT, SMDI)
tc1 - texture coordinates for second "wrap" (for textures AS, MC)
norm - vertex normal line
tanX, tanY - tangent-space for first "wrap" (for example of settings see interface picture below)
Material parameters (Super_01.cgfx Parameters)
show final color of material - shows unlit resulting color of material
show world-space normals - shows reverse normal map
show fresnel - at model it shows intensity of reflections in gray scale according to set 'fresnel' parameters
use sRGB conversions - on input are textures converted into linear space, in which are carried calculations and result is again converted to sRGB
use texture coords 2 - for selected textures (MC, AS) is used second mapping
ambient, diffuse, forced diffuse, specular - colors of material components; they have same meaning as in material editor Objektiv2
specular power - specular strength
TEXTURES
(COLOR, NORMAL, DETAIL, MACRO, AMBIENT, SPECULAR, ENVIRONMENTAL)
For each texture there is parameter fader which blends betweensubstitute color and texture. This solution replaces procedural textures. Fader setting to 0 means that it will use only substitute color while setting mean it will use only texture. For NORMAL map there is no substitute color setup as it is hardset to RGB=(0.5, 0.5, 1.0), which is default normal line direction (upright to surface). With fader it is possible test various "strength" of normal map (values higher than 1 increasing influence while smaller decreasing influence) and then eventually alter texture. For DETAIL map the situation is similar, substitute color is hardset to RGB=(0.5, 0.5, 1.0) and you can define by fader different strength.
Example setting up procedural color map "#(argb,8,8,3)color(0.5,0.5,0.5,1,CO)": "COLOR MAP fader" set to 0, "color" set to 50% šedou and "(alpha)" to 1
environ. map multiplier - environmental map multiplier (tuning parameter related to lighting)
FRESNEL
Fresnel calculation with help of coefficients N and K is not suitable for intgration into CgFX shaderu therefore it is replaced by simpler variants which fails to naturally represent curve for metal materials. fresnel R0 - specular strength on surface upright to direction of sight fresnel grade - curve "steepness"
detailTcMulX, detailTcMulY - mapping multiplier for detail texture
Illumination model
ambient lighting ON, diffuse lighting ON, specular lighting ON, specular environmental lighting ON - tuning switches of lighting model's individual components
global light multiplier - multiplier of all lights
HEMISPHERICAL LIGHT
hemispheric light ON - light switch
sky light - color and intensity of light from top hemisphere
ground light - color and intensity of light from top hemisphere
DIRECTIONAL LIGHT
dir light ON - light switch
bi-dir light ON - contrejour light switch (something like reflection)
dir light direction - link up directional light in scene (right mouse button click and choose correct light)
dir light color - light color and intensity
bi-dir color - color of material from which contrejour light reflects
dir light multiplier - directional light multiplier
POINT LIGHT
point light ON - light switch
point light per-pixel - enable more precise lighting calculation (for testing only; it is not part of super shader)
point light position - link up point light in scene (right mouse button click and choose correct light)
point light color - light color and intensity ?of directional light component?
point light ambient - ambient component color and intensity (depends only on distance not direction)
point light multiplier - light intensity multiplier
point light attenuation - coefficient for intensity decline with distance (more precisely reverse value - the higher value, the bigger afterglow)
Picture with interface of super-shader material inside Maya:
Super Shader FX for Autodesk 3DS Max
Shader usage
Display driver for 3DS Max must be set to DirectX 9.0 to be able use shader. To create new material dot his: Within Material editor choose free slot and set material type to "DirectX 9 Shader" (instead default "Standard"). Then is needed set path to file "SuperShader.fx" inside tab "DirectX 9 Shader". When file is loaded it will show material parameters within tab "SuperShader.fx Parameters" (see appended picture).
Picture with interface of super-shader material inside 3DS Max:
"Technique"
Each fx-file may include multiple techniques. For alpha blending i use standalone technique because it is not possible do with just checkbox field.
SuperShader_Default - for opacity geometry
SuperShader_AlphaBlend - for transparent geometry; often hard to sort and nothing can be done about it
SuperShader_MapTest - with help of parameters "map test CO alpha" till "map test ENVIR" shows on model particular texture or it is component (it's used only downmost checked option - doesn't go other way at present time; options "map test" works only in this technique
Illumination model
Material can be assigned one directional and one point lighting (parameters "dir light direction" and "point light position"). Color and intensity is taken directly from light.
rest is nearly same as here: Super shader#Super shader inside CgFX for Autodesk Maya
How is gained fresnel from procedural texture
Procedural texture for fresnel function contains single-dimensional conversion table (visually it is sort of brightness gradient ) from which reads value on position (U,V). Value U is calculated as scalar product between normal line and direction to the camera (both vertors must be normalized)) in each surface point of model (this value also represents cosine of angle between vectors). Value V is always 0.5, therefore it is unneeded that texture height would be different than 1. For example: function with parameters N = 1.0 and K = 0.6 should be entered with width 64 and height 1: "#(ai,64,1,1)fresnel(1,0.6)". Size of texture is then only 64 bytes instead 4096 in case if the height is 64. When we realize that such texture is generated for every material with fresnel inside scene, then saving of memory and performance is indispensable!
Picture with visual representation of obtaining fresnel value from procedural texture: