Chernarus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
North-Eastern Chernarus is a hilly area with rocky coastlines; the biggest hilltops reach over 700 m above sea level, covered by temperate forests. The environment is still relatively untouched from logging and mining. The biggest cities and industry are concentrated on the southern coast. There are mostly smaller villages inland, situated in deep valleys, hidden in forested ridges or on elevated plateaus with lush meadows. | North-Eastern Chernarus is a hilly area with rocky coastlines; the biggest hilltops reach over 700 m above sea level, covered by temperate forests. The environment is still relatively untouched from logging and mining. The biggest cities and industry are concentrated on the southern coast. There are mostly smaller villages inland, situated in deep valleys, hidden in forested ridges or on elevated plateaus with lush meadows. | ||
First settlements date back to 5th Century B.C. When the valleys of the Burnaja and Svetlaya rivers were inhabited by Skyth tribes and nomads, who later formed the Takmyr and Karzeg nations. The center of modern Chernarus had been founded in the delta of the Burnaya River and on the coast, divided from the Zagorie region which was under the supremacy of a Moscow Principate by the Black Mountains ridge. | |||
The local Slavic population constantly had to fight off the raiders from the southwest so it was traditionally bound with Russia, but always kept its independence. In the 12th Century it was controlled by dukes, in the 13th century it was united by Taras Kozub. The Kozub dynasty ruled until 1631, when Chernarus joined the Russian empire. After the revolution in 1917 Chernarus became an autonomic federal republic, after the demise of the USSR in 1991 it gained independence. | |||
==General Information== | ==General Information== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 19: | ||
*Hilly rural landscape with rocky coastline | *Hilly rural landscape with rocky coastline | ||
*Living environment including civilian population and wildlife | *Living environment including civilian population and wildlife | ||
==About== | |||
===Old Sights=== | |||
Chernarus has lots of old castle ruins, keeps and fortresses, which were built at the turn of the 11th and 12th century by Duke Kozlov, for the means of protecting important roads and grounds, which were often attacked from the sea and by northern neighbors. The Pik Kozlova above the Chernogorsk city is named after this duke, who is considered a founder of the first Chernarussian state. On the peak above the city there used to stand a warning post which protected the local provinces from pirate raids. This rocky peak is a favorite lookout point nowadays. | |||
The majority of the structures of that time were made of wood, only the ruins of Rog keep and the famous Devil's Castle are preserved to this day. The Devil's Castle received its name many years later, perhaps sometime during the end of the 13th century. After the fall of Kozlov's Principate at the beginning of the 13th century, the fortress system fell apart; fortresses that weren't burned down were taken apart stone by stone, as needed for the structure of surrounding estates, or for different purposes. | |||
The former Kozlovo Castle, now called the Devil's Castle, was supposedly inhabited by the yeoman Jakub Čert (Devil) from Gorka. His bandit campaigns started here at the castle. He enlarged the keep of the castle, using the loot from these raids and the castle holds his name to this day. According to legend, the Devil's Castle was burned down during the zagorian Karzeg's rebellion, Jakub Čert burned in the castle's main tower after he refused to surrender to Ataman Simurg. Only burned walls remain of the castle, haunted to this day by the spirit of Ivan Kozlov. Whatever the truth is, Devil's Castle is one of the most remarkable architectural sights in Chernarus and it became a rewarding destination for tourists. | |||
===Military Zones=== | |||
Shortly after WWII, the small Red Army airport in the Northern province, designated for parachute training, expanded and gradually evolved into an air base with large military surroundings. In the border mountains there are a few former bases. After the regaining of independence, the Chernarussian Army took over these military bases. | |||
At present, there is a lack of funds needed for security and maintenance; the condition of these bases has become even worse because of fighting between the regular army and rebel units who were using a number of these bases as their foot-holds. Visiting the former military areas isn't forbidden, but due to large numbers of unexploded ordnance as well as the decayed conditions of the buildings it is not recommended. | |||
===Nature=== | |||
Despite the industrialization and the devastation of the coast, the Northern Province is proud of its untouched wild nature and idyllic agriculture countryside. Mostly because of the highland character of the North East part of the country, this was unsuitable for either industrial production or for collective agriculture. | |||
A large part of the northern area is covered by coniferous or mixed forests, known as the Black forests because of their depth and inviolateness. The unique moors on the table-side Dičina on the south of the Vybor is also worth mentioning. In the scientific view the area around the Blunt rocks is very precious: rock formations with the remains of a glacial lake from ice age times. The southern part of the Northern Province suffered through thoughtless construction, so that the original coastal fauna and flora can only be found sporadically, mostly aside the mainland. The best known such place is the Skalistý Island, which during the start of the 90's was declared a nature preserve within the frame of the newly declared Zagorie Protected Natural Area. | |||
===Industrial Areas=== | |||
For the fast growing industrial production in the second half of the 20th century, the electricity inflow conducted by land from the west was insufficient; also the basic infrastructure of gravel roads was inconvenient. Yearly floods, created from the melting snow were constantly threatening the coastal railroad, built for the purpose of transporting cargo from Chernogorsk to the industrial centers. This was the only secure connection during the long-lasting rains. | |||
In the 70's it was decided to build a motorway infrastructure and also construct a number of waterworks, which would not only reduce the yearly floods, but also allow the generation of electricity from owned sources. The results of this effort are mainly the Pobeda Dam, a number of flood barriers on the main traffic artery leading from Chernogorsk along the coast to Berezin, and of course the great hydro-electric power plant near Elektrozavodsko. | |||
===Inhabited Areas=== | |||
The biggest city and the administrative center of the Chernarussian Northern Province is Chernogorsk. What was originally a small fisherman's village quickly grew into a city thanks to the intensive industrialization of the Chernarussian Autonomic Republic, which began in the 50's of the previous century. Chernogorsk has always been a harbor town, once connected to northern trade routes, now a place through which the raw materials flow to Elektrozavodsk. | |||
By the decision of the Soviet Union's government, not only Chernogorsk, but also other fairly undeveloped cities of the Northern Province were supposed to change to the symbol of industrial advancement. The price for urbanization and industrialization was the environmental damage of the coastal areas. The local village population was rooted out and forced to live an urban life, or moved to the northern Kolkhozs. This fact reflects not only in the fast-engineered infrastructure and generic apartment block style housing developments, but also in the architectural spirit of socialistic realism. The dominants of the cities then aren't the historical centers, but industrial zones, lime-kiln and the buildings of long abandoned factories. | |||
==Major citys== | |||
*Chernogorsk | |||
*Electrozavodsk | |||
*Stary Sobor | |||
*Zelenogorsk | |||
*Solnichniy | |||
*Vybor | |||
*Gorka | |||
*Berezino | |||
*Krasnostav | |||
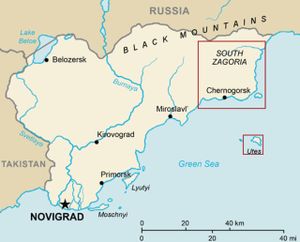
==Maps== | ==Maps== | ||
{| border="0" cellspacing="0" style="padding: 0px;" | {| border="0" cellspacing="0" style="padding: 0px;" | ||
| Line 22: | Line 74: | ||
|[[Image:arma_2_island_locations.jpg|thumb|Map showing all of Chernarus]] | |[[Image:arma_2_island_locations.jpg|thumb|Map showing all of Chernarus]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
Revision as of 11:44, 23 October 2009
„Chernarus is a fictional post-Soviet country, accurately recreated from geographical data of real landscape.“
North-Eastern Chernarus is a hilly area with rocky coastlines; the biggest hilltops reach over 700 m above sea level, covered by temperate forests. The environment is still relatively untouched from logging and mining. The biggest cities and industry are concentrated on the southern coast. There are mostly smaller villages inland, situated in deep valleys, hidden in forested ridges or on elevated plateaus with lush meadows.
First settlements date back to 5th Century B.C. When the valleys of the Burnaja and Svetlaya rivers were inhabited by Skyth tribes and nomads, who later formed the Takmyr and Karzeg nations. The center of modern Chernarus had been founded in the delta of the Burnaya River and on the coast, divided from the Zagorie region which was under the supremacy of a Moscow Principate by the Black Mountains ridge.
The local Slavic population constantly had to fight off the raiders from the southwest so it was traditionally bound with Russia, but always kept its independence. In the 12th Century it was controlled by dukes, in the 13th century it was united by Taras Kozub. The Kozub dynasty ruled until 1631, when Chernarus joined the Russian empire. After the revolution in 1917 Chernarus became an autonomic federal republic, after the demise of the USSR in 1991 it gained independence.
General Information
- Chernarus is based on actual real world data
- Chernarus is 225 km2 in size
- Almost 100km2 of Chernarus is covered by forest
- Chernarus has 350 kilometers of roads
- There are a total of 50 towns and villages across Chernarus
- Chernarus has three airfields (1 big and 2 small)
- 1 million 3d objects
- Hilly rural landscape with rocky coastline
- Living environment including civilian population and wildlife
About
Old Sights
Chernarus has lots of old castle ruins, keeps and fortresses, which were built at the turn of the 11th and 12th century by Duke Kozlov, for the means of protecting important roads and grounds, which were often attacked from the sea and by northern neighbors. The Pik Kozlova above the Chernogorsk city is named after this duke, who is considered a founder of the first Chernarussian state. On the peak above the city there used to stand a warning post which protected the local provinces from pirate raids. This rocky peak is a favorite lookout point nowadays.
The majority of the structures of that time were made of wood, only the ruins of Rog keep and the famous Devil's Castle are preserved to this day. The Devil's Castle received its name many years later, perhaps sometime during the end of the 13th century. After the fall of Kozlov's Principate at the beginning of the 13th century, the fortress system fell apart; fortresses that weren't burned down were taken apart stone by stone, as needed for the structure of surrounding estates, or for different purposes.
The former Kozlovo Castle, now called the Devil's Castle, was supposedly inhabited by the yeoman Jakub Čert (Devil) from Gorka. His bandit campaigns started here at the castle. He enlarged the keep of the castle, using the loot from these raids and the castle holds his name to this day. According to legend, the Devil's Castle was burned down during the zagorian Karzeg's rebellion, Jakub Čert burned in the castle's main tower after he refused to surrender to Ataman Simurg. Only burned walls remain of the castle, haunted to this day by the spirit of Ivan Kozlov. Whatever the truth is, Devil's Castle is one of the most remarkable architectural sights in Chernarus and it became a rewarding destination for tourists.
Military Zones
Shortly after WWII, the small Red Army airport in the Northern province, designated for parachute training, expanded and gradually evolved into an air base with large military surroundings. In the border mountains there are a few former bases. After the regaining of independence, the Chernarussian Army took over these military bases.
At present, there is a lack of funds needed for security and maintenance; the condition of these bases has become even worse because of fighting between the regular army and rebel units who were using a number of these bases as their foot-holds. Visiting the former military areas isn't forbidden, but due to large numbers of unexploded ordnance as well as the decayed conditions of the buildings it is not recommended.
Nature
Despite the industrialization and the devastation of the coast, the Northern Province is proud of its untouched wild nature and idyllic agriculture countryside. Mostly because of the highland character of the North East part of the country, this was unsuitable for either industrial production or for collective agriculture.
A large part of the northern area is covered by coniferous or mixed forests, known as the Black forests because of their depth and inviolateness. The unique moors on the table-side Dičina on the south of the Vybor is also worth mentioning. In the scientific view the area around the Blunt rocks is very precious: rock formations with the remains of a glacial lake from ice age times. The southern part of the Northern Province suffered through thoughtless construction, so that the original coastal fauna and flora can only be found sporadically, mostly aside the mainland. The best known such place is the Skalistý Island, which during the start of the 90's was declared a nature preserve within the frame of the newly declared Zagorie Protected Natural Area.
Industrial Areas
For the fast growing industrial production in the second half of the 20th century, the electricity inflow conducted by land from the west was insufficient; also the basic infrastructure of gravel roads was inconvenient. Yearly floods, created from the melting snow were constantly threatening the coastal railroad, built for the purpose of transporting cargo from Chernogorsk to the industrial centers. This was the only secure connection during the long-lasting rains.
In the 70's it was decided to build a motorway infrastructure and also construct a number of waterworks, which would not only reduce the yearly floods, but also allow the generation of electricity from owned sources. The results of this effort are mainly the Pobeda Dam, a number of flood barriers on the main traffic artery leading from Chernogorsk along the coast to Berezin, and of course the great hydro-electric power plant near Elektrozavodsko.
Inhabited Areas
The biggest city and the administrative center of the Chernarussian Northern Province is Chernogorsk. What was originally a small fisherman's village quickly grew into a city thanks to the intensive industrialization of the Chernarussian Autonomic Republic, which began in the 50's of the previous century. Chernogorsk has always been a harbor town, once connected to northern trade routes, now a place through which the raw materials flow to Elektrozavodsk.
By the decision of the Soviet Union's government, not only Chernogorsk, but also other fairly undeveloped cities of the Northern Province were supposed to change to the symbol of industrial advancement. The price for urbanization and industrialization was the environmental damage of the coastal areas. The local village population was rooted out and forced to live an urban life, or moved to the northern Kolkhozs. This fact reflects not only in the fast-engineered infrastructure and generic apartment block style housing developments, but also in the architectural spirit of socialistic realism. The dominants of the cities then aren't the historical centers, but industrial zones, lime-kiln and the buildings of long abandoned factories.
Major citys
- Chernogorsk
- Electrozavodsk
- Stary Sobor
- Zelenogorsk
- Solnichniy
- Vybor
- Gorka
- Berezino
- Krasnostav
Maps
External Links
Interactive map of Chernarus (Arma2.com)
Chernarus PDF (Arma2.com)
Chernarus: South Zagoria 3 sized hi-res JPG images (forums.bistudio.com)