PAA File Format: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
m (→FLAGTAGG) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
{ | { | ||
char " | char "GGATGALF"; | ||
ulong len; // 4 bytes | ulong len; // 4 bytes | ||
ulong range; // 0 to 2 | ulong range; // 0 to 2 | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
Marks if texture contains transparency. Value 1 means basic transparency, 2 means alpha channel is not interpolated. This flag should be always present in LOD textures with 1-bit alpha with value of 2 or there will be "ghost outlines" on LOD textures when viewed from distance. Note that this flag must be present in texture file when binarizing model, because Binarize stores information about how to render textures in actual P3D file. | Marks if texture contains transparency. Value 1 means basic transparency, 2 means alpha channel is not interpolated. This flag should be always present in LOD textures with 1-bit alpha with value of 2 or there will be "ghost outlines" on LOD textures when viewed from distance. Note that this flag must be present in texture file when binarizing model, because Binarize stores information about how to render textures in actual P3D file. | ||
===MAXCTAGG=== | ===MAXCTAGG=== | ||
Revision as of 04:12, 21 March 2010
PAA texture file structure
Introduction
Of the many image file formats 'out there', such as jpeg, such as gif. BI choose to use a specially developed file format (paa) as the base texture file for all engine types.
The reason for this is the raw data within the file can be passed directly to Microsoft's Direct X as a DXT1 picture (eg) without further massaging.
While all engines except Elite also support JPG files, PAA files can result in much better performance.
Main Format
Overall structure of a Paa file is
struct overall
{
ushort TypeOfPaa; //OPTIONAL
Tagg Taggs[...]; //OPTIONAL
Pallette Pallette[...]; //OPTIONAL
MipMap MipMaps[...];
ushort Always0;
};
TypeOfPaa (optional)
all files except the Index Palette starts with a TypeOfPaa texture
- 0xFF01 DXT1 compressed texture (may have 1 bit alpha map, check MSDN documentation for details)
- 0xFF02 DXT2 compressed texture (Oxygen 2)
- 0xFF03 DXT3 compressed texture
- 0xFF04 DXT4 compressed texture (Oxygen 2)
- 0xFF05 DXT5 compressed texture
- 0x4444 Uncompressed RGBA 4:4:4:4 texture
- 0x1555 Uncompressed RGBA 5:5:5:1 texture
- 0x8888 Uncompressed RGBA 8:8:8:8 texture (Oxygen 2)
- 0x8080 Uncompressed Luminosity/Alpha map. Actual color of texture is derived from AVGCTAGG tag?
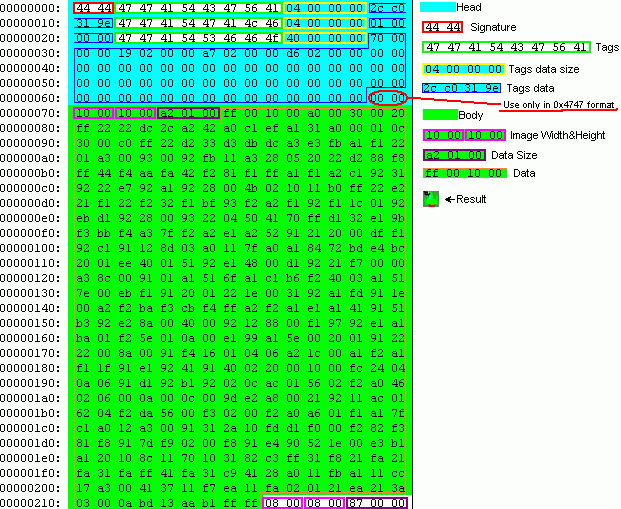
- 0x4747 Uncompressed Index Palette texture(P8) SPECIAL CASE see notes
Special Case
Uncompressed Index Palette texture
This type of paa file has NO 'type'. TagData is immediate. The next block of data after HeaderTags (if any) is the palette. Followed by 'non-standard' mip-data blocks.
Taggs
Tagg
{
char name[8]; // NOT ASCIIZ name of tag is reversed when written in file, OFFSTAGG written as GGATSFFO
ULONG DetaLen;
byte data[DetaLen];
}
header tags continue until un-decipherable. Eg the TAG is not known. In which case either pallete or mip data follows
AVGCTAGG
Average Colour
This tag contains average color of texture, probably used in rendering 8:8 luminosity/alpha textures.
{
char "GGATCGVA";
ulong len; // 4 bytes
ulong RGBA;//FF443D39
}
FLAGTAGG
{
char "GGATGALF";
ulong len; // 4 bytes
ulong range; // 0 to 2
}
Marks if texture contains transparency. Value 1 means basic transparency, 2 means alpha channel is not interpolated. This flag should be always present in LOD textures with 1-bit alpha with value of 2 or there will be "ghost outlines" on LOD textures when viewed from distance. Note that this flag must be present in texture file when binarizing model, because Binarize stores information about how to render textures in actual P3D file.
MAXCTAGG
{
char "GGATCXAM";
ulong len; // 4 bytes
ulong data; // FFFFFFFFF no other value seen so far
}
Contains color of brightest pixel in texture?
SWIZTAGG
{
char "GGATZIWS";
ulong len; // 4 bytes
ulong data; // 0x05040203
}
Swizzle is apparently used to modify texture components processing like swizzle modifiers in pixel shaders. For example ArmA sky texture has green channel stored in alpha channel and inversed to take advantage from feature that in DXT5 64 bits are used for alpha channel in each block and 64 bits for RBG, giving double the accuracy to green channel as opposed to storing texture just normally.
Exact format of swizzle data is still unknown. swizzle data:
char channelSwizzleA; char channelSwizzleR; char channelSwizzleG; char channelSwizzleB;
format of swizzle char:
bits 7-4 = 0; bit 3 - "1" flag. All channel data must be set to 0xff; bit 2 - "negate flag". Channel data must be negated. bit 1-0 - number of color channel: 00 - Alpha channel 01 - Red channel 10 - Green channel 11 - Blue channel
for example (*_nohq.paa textures)
swizzle data is:
0x05 - Alpha, Negated, stored in Red; 0x04 - Red, Negated, stored in Alpha; 0x02 - Green, Stored as is; 0x03 - Blue, Stored as is;
PROCTAGG
{
char "GGATCORP";
ulong len; // strlen(text)
char text // NOT ASCIIz
}
this is a non asciiz string (not zero terminated)
example:
x = ((u+1)*0.5);
y = ((v+1)*0.5);
if (y<0.5) then
{
sharpOut = 20;
sharpIn = 60;
offset = x-0.5;
if (offset<0) then
{
edge = (1+offset)^sharpOut;
}
else
{
edge = (1-offset)^sharpIn;
};
res = edge*y*2;
}
else
{
sharpOut = 20-40*(y-0.5);
sharpIn = 60-125*(y-0.5);
offset = x-0.5;
if (offset<0) then
{
edge = (1+offset)^sharpOut;
}
else
{
edge = (1-offset)^sharpIn;
};
res = edge;
sdCoef = y * 2 - 1;
shoreDisappear = 1 - sdCoef^2;
res = res * shoreDisappear;
};
a = 1;
r = res;
g = res;
b = res;
OFFSTAGG
{
char "GGATSFFO";
ulong len; // 16 * sizeof(ulong)
ulong offsets[16];
}
Example: = 6 entries. last 10 unused 256 x 128 Size=16384 128 x 64 Size=4096 64 x 32 Size=1024 32 x 16 Size=256 16 x 8 Size=64 8 x 4 Size=16
MipMap data is presented in 'blocks'. One or more 'blocks' exist in a paa file.
This tag declares where each of these blocks are in the file, relative to start of file.
The location of each block is already known, relative to the size of the previous block (if any). So, although almost always present in paa files, it's use, is redundant.
This tag always contains 16 ULONG offsets. Each one is a hard offset to actual mipmap data relative to start of file.
Not all entries are used (obvuously) since most paa files contain less than 16 mipmaps. Unused offsets contain the value 0x00000000. There are no known examples of splattered offset entries. All offsets after the first 0 entry are 0 as well.
Pallette
Pallette
{
ushort nPalletTriplets; // 0 except for index pallette type
bytes RGB_Pallet[nPalletTriplets][3]; // ie zero normally
}
pallette triplets when they exist, consist of GBR values
Normal Mipmaps
Mipmaps are in contiguous blocks that extend to end of file.
Mipmap
{
ushort width; // width of this mipmap
ushort height; // height of this mipmap
if (width and height)
{
byte size[3]; // size of texture data in file. this is 24-bit unsigned integer.
byte data[size]; // actual texture data compressed or otherwise
}
};
The last mipmap is a dummy consisting of zero width and height with NO FURTHER DATA
- Note that the size reflects the size of data in the file not the actual size if that data if is compressed.
Tag OFFSTAGG (if supplied) contains (up to) 16 offsets. Each of those offsets point succsessive mipmap blocks (relative to start of the file).
The size of output data for Dct1 format is (width*height / 2)
Size of output data for Dct5 format is (width*height)
DXT1 textures are stored "as is" ( see ->DXTn compress/decompress).
Pallette MipMap
IndexMipMap
{
ulong color; // perhaps
if (color)
{
MipMap MipMap;
}
}
Similar to a standard mipmap, each one is preceeded by a color.
The LAST pallette mipmap contains 0 color. WITH NO FURTHER DATA
Addenda
Decompression Code
/*
by Flea
*/
int LZSSDecode(unsigned char * in,unsigned char * out,int szin,int szout)
{
szin = szin > 0? szin: 0x7fffffff;
int i, j, k, r = 0, pr, pi = 0,po = 0;
unsigned int flags = 0;
unsigned char buf[0x100F], c;
for (i = 0; i < 0x100F; buf[i] = 0x20, i++);
while (pi < szin && po < szout)
{
if (((flags >>= 1) & 256) == 0)
{
if(pi >= szin)break;
c = in[pi++];
flags = c | 0xff00;
}
if (flags & 1)
{
if(pi >= szin || po >= szout)break;
c = in[pi++];
out[po++] = c;
buf[r++] = c;
r &= 0xfff;
} else
{
if(pi + 1 >= szin)break;
i = in[pi++];
j = in[pi++];
i |= (j & 0xf0) << 4;
j = (j & 0x0f) + 2;
pr = r;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
{
c = buf[(pr - i + k) & 0xfff];
if(po >= szout)break;
out[po++] = c;
buf[r++] = c;
r &= 0xfff;
}
}
}
return pi;
}
HexDump
Alpha channel interpolation
These two images visualize difference between alpha channel interpolation (FLAGTAGG header tag value).
FLAGTAGG = 1, interpolated alpha channel (default behaviour)
FLAGTAGG = 2, alpha channel interpolation disabled
Bibliography
Feersum's original posting on BIS forums: Paa/pac texture format documentation MSDN documentation on DXT1 textures: DirectX: Opaque and 1-Bit Alpha Textures Squish Compression DXTn compress/decompress