Modding Structure – DayZ
Category: DayZ: Modding Structure
m (added missing parameter for skeletonDefinitions) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC|side}} | |||
This page details the structure of DayZ mods as well as their configuration and presentation. | |||
== Mod structure == | == Mod structure == | ||
Mod is loaded using the '''-mod=''' launch parameter | Mod is loaded using the '''-mod=''' launch parameter | ||
''-mod=C:\MyMods\TestMod'' | |||
''-mod=C:\MyMods\TestMod'' | |||
Typical mod folder downloaded from steam workshop will contain: | Typical mod folder downloaded from steam workshop will contain: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 14: | ||
* '''mod.cpp''' optional config file, holds information for mod presentation | * '''mod.cpp''' optional config file, holds information for mod presentation | ||
[[Image:dayz_modstructure.png]] | |||
== PBO structure == | == PBO structure == | ||
The only required part of .pbo is '''config.cpp''': | |||
The only required part of .pbo is '''config.cpp''' | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | |||
class CfgPatches // required | class CfgPatches // required | ||
{ | { | ||
| Line 37: | Line 27: | ||
requiredAddons[]= | requiredAddons[]= | ||
{ | { | ||
"DZ_Data", | "DZ_Data", // addon depedency | ||
}; | }; | ||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 46: | Line 36: | ||
class TestMod | class TestMod | ||
{ | { | ||
type = "mod"; // required | |||
inputs = "mods\testmod\inputs\my_new_inputs.xml"; | inputs = "mods\testmod\inputs\my_new_inputs.xml"; // optional, when using custom inputs | ||
dependencies[]={"Game"}; | skeletonDefinitions = "mods\testmod\skeleton\skeletons.xml"; // optional, when using custom skeletons.anim.xml | ||
dependencies[]={"Game"}; // optional, when you need to set class dependency | |||
class defs | |||
{ | |||
// optional: you can add custom imagesets like this | |||
class imageSets | |||
{ | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/gui/imagesets/mod1.imageset", "mods/testmod/gui/imagesets/mod2.imageset" }; | |||
}; | |||
// optional: you can add custom widget styles like this | |||
class widgetStyles | |||
{ | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/gui/looknfeel/mod1.styles", "mods/testmod/gui/looknfeel/mod2.styles"}; | |||
}; | |||
class engineScriptModule | |||
{ | |||
value=""; // when value is empty, default entry function is used | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/1_Core"}; // you can add any number of files or directories and they will be compiled together with original game module scripts | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
/* | |||
script module config classes are optional, define only what you want to mod | |||
class gameLibScriptModule | |||
{ | |||
value=""; | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/2_GameLib"}; | |||
};*/ | |||
class gameScriptModule | |||
{ | |||
value="CreateGameMod"; // when value is filled, default script module entry function name is overwritten by it | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/3_Game"}; | |||
}; | |||
class worldScriptModule | |||
{ | |||
value=""; | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/4_World"}; | |||
}; | |||
== | class missionScriptModule | ||
{ | |||
value=""; | |||
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/5_Mission"}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
}; | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
The internal structure is largely up to the modders themselves, e.g. in case of script files, it doesn't matter where they are placed as long as they are in their respective script module and paths are set properly. | |||
== Mod presentation == | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | Configured through '''mod.cpp''' in the mod root folder, used for mod presentation in the main menu of the game: | ||
name = "Mod name"; // name | <syntaxhighlight lang="cpp"> | ||
name = "Mod name"; // name | |||
picture = "Mods/TestMod/modpic.tga"; // picture in expanded description | picture = "Mods/TestMod/modpic.tga"; // picture in expanded description | ||
logoSmall = "Mods/TestMod/modlogosmall.tga"; // icon next to mod name when description is not expanded | logoSmall = "Mods/TestMod/modlogosmall.tga"; // icon next to mod name when description is not expanded | ||
logo = "Mods/TestMod/modlogo.tga"; // logo below game menu | logo = "Mods/TestMod/modlogo.tga"; // logo below game menu | ||
logoOver = "Mods/TestMod/modlogohover.tga"; // on mouse hover over logo | logoOver = "Mods/TestMod/modlogohover.tga"; // on mouse hover over logo | ||
tooltip = "tooltip"; // tool tip on mouse hover | tooltip = "tooltip"; // tool tip on mouse hover | ||
overview = "Bestest mod"; // overview | overview = "Bestest mod"; // overview | ||
| Line 121: | Line 108: | ||
version = "1.5"; // version | version = "1.5"; // version | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
{{GameCategory|dayz|Modding Structure}} | |||
Latest revision as of 06:46, 3 August 2021
This page details the structure of DayZ mods as well as their configuration and presentation.
Mod structure
Mod is loaded using the -mod= launch parameter
-mod=C:\MyMods\TestMod
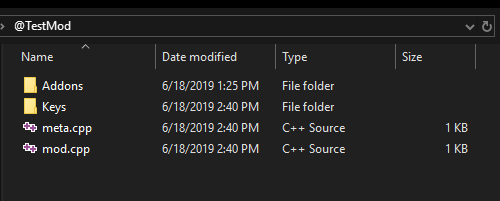
Typical mod folder downloaded from steam workshop will contain:
- Addons folder, holds the mod's .pbo files
- Keys folder, contains public .bikey used to sign the .pbo files (required for client-server signature verification)
- meta.cpp file, holds workshop meta data (will be automatically created during mod publishing)
- mod.cpp optional config file, holds information for mod presentation
PBO structure
The only required part of .pbo is config.cpp:
class CfgPatches // required
{
class TestMod
{
requiredAddons[]=
{
"DZ_Data", // addon depedency
};
};
};
class CfgMods // required in pbo's which add/modify scripts or inputs
{
class TestMod
{
type = "mod"; // required
inputs = "mods\testmod\inputs\my_new_inputs.xml"; // optional, when using custom inputs
skeletonDefinitions = "mods\testmod\skeleton\skeletons.xml"; // optional, when using custom skeletons.anim.xml
dependencies[]={"Game"}; // optional, when you need to set class dependency
class defs
{
// optional: you can add custom imagesets like this
class imageSets
{
files[]={"mods/testmod/gui/imagesets/mod1.imageset", "mods/testmod/gui/imagesets/mod2.imageset" };
};
// optional: you can add custom widget styles like this
class widgetStyles
{
files[]={"mods/testmod/gui/looknfeel/mod1.styles", "mods/testmod/gui/looknfeel/mod2.styles"};
};
class engineScriptModule
{
value=""; // when value is empty, default entry function is used
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/1_Core"}; // you can add any number of files or directories and they will be compiled together with original game module scripts
};
/*
script module config classes are optional, define only what you want to mod
class gameLibScriptModule
{
value="";
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/2_GameLib"};
};*/
class gameScriptModule
{
value="CreateGameMod"; // when value is filled, default script module entry function name is overwritten by it
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/3_Game"};
};
class worldScriptModule
{
value="";
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/4_World"};
};
class missionScriptModule
{
value="";
files[]={"mods/testmod/scripts/5_Mission"};
};
};
};
};
The internal structure is largely up to the modders themselves, e.g. in case of script files, it doesn't matter where they are placed as long as they are in their respective script module and paths are set properly.
Mod presentation
Configured through mod.cpp in the mod root folder, used for mod presentation in the main menu of the game:
name = "Mod name"; // name
picture = "Mods/TestMod/modpic.tga"; // picture in expanded description
logoSmall = "Mods/TestMod/modlogosmall.tga"; // icon next to mod name when description is not expanded
logo = "Mods/TestMod/modlogo.tga"; // logo below game menu
logoOver = "Mods/TestMod/modlogohover.tga"; // on mouse hover over logo
tooltip = "tooltip"; // tool tip on mouse hover
overview = "Bestest mod"; // overview
action = "https://dayz.com/"; // link
author = "modguy"; // author
version = "1.5"; // version