CrashDome/Sandbox – User
FSM file structure and Concepts
Introduction
The FSM file is a new edition to Bohemia Interactive products starting with the Armed Assault and VBS2 product lines. FSM stands for Finite State Machine and is the primary method of coordinating Artificial Intelligence within these products.
What is the purpose of a Finite State Machine?
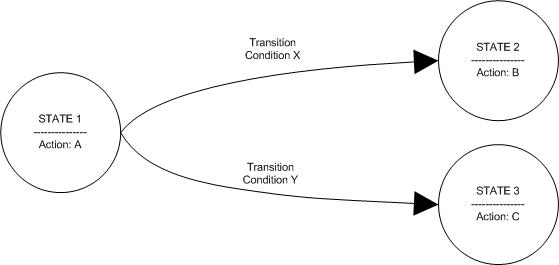
A Finite State Machine (as defined on Wikipedia) "is a model of behavior composed of states, transitions and actions."
By allowing an object to change states, we can give the appearance of dynamics. By allowing an object to change states conditionally, we can give the appearance of not only dynamics, but also intelligence.
As an object changes states, we perform actions which emit the desired behavior of that state. As in the above example, an object might start in State 1 and perform Action A. After the action is performed, the state machine looks at the next possible transitions and tries to find the transition in which a condition is satisfied. Perhaps in the above example, our object finds Condition Y is satisfied. In this case, the object would enter State C and perform Action C. In this crude example, the state machine would exit and our example would be complete. In more elaborate examples there might exist a transition which would take our object from State C to some other state such as back to State A - or even back to itself to perform the Action C again.
File Format
Bohemia Interactive's FSM file format is similar in syntax to other "class" containing files such as the Description.ext file or the config.cpp file.
Class FSM
{
fsmName = “”;
initState = “”;
finalStates[] = {};
Class States
{
class SampleState
{
name=””;
init=””;
class Links
{
class SampleLink
{
priority=0.000000;
to=””;
condition=””;
action=””;
};
};
};
};
};
FSM Class
The FSM class contains three properties and a collection of States.
- fsmName: This property takes a string argument and defines the name of the FSM.
- initState: This property takes a string argument and refers the engine to begin at a predefined state in the state collection.
- finalStates: This property takes an array of string arguments. Current purpose unkown.
State Class
The State Class is the definition of a single state and the actions it performs. This class contains two properties and a collection of Links.
- name: This property takes a string argument and defines the name of the state.
- init: This property takes a string argument and represents the code executed upon an objects entering of the state. The code follows standard coding guidelines for Functions or the code type.
Link Class
The Link Class contains 4 properties.
- priority: This property is a floating point number which defines in what order the engine is to check conditions. A high value indicates higher priority.
Example: A link with the priority value of 1 exists along with another link which has a priority of 0. Even though both might contain different conditions, both could have satisfied conditions when the machine is looking for a state change (both conditions evaluate true). In this case, the priority of 1 will become the transition chosen.
- to: This property takes a string argument and defines the destination of the Link. The string should match the string of the destination State's name definition.
- condition: This property takes a string argument and is a code statement which must evaluate to true or false
Example: (side player == West)
- action: This property also takes a string argument and defines code to execute during the transition (prior to state change). The code follows standard coding guidelines for Functions or the code type.
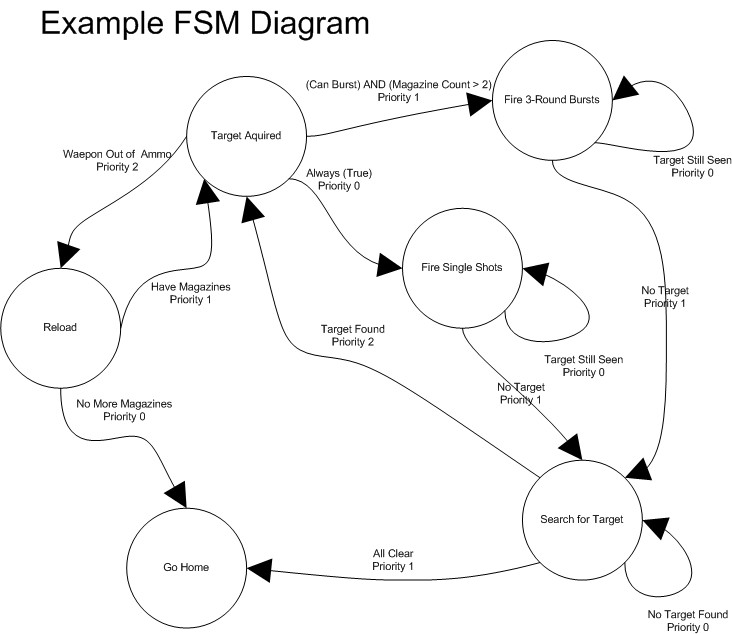
Concepts and Examples
Generic Example
Bibliography
crashdome: