Audio: Technical Fundamentals – Arma Reforger
This page aims to give a high-level understanding of how the audio pipeline within (and from) Arma Reforger works.
The Audio Pipeline
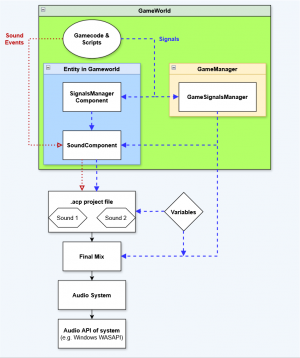
Depicted is a high-level overview of the game's audio pipeline. Below is a short explanation of its inner workings. In order to understand it better, there are more elaborate explanations for each element further below, with some leading to dedicated pages.
Elements Rundown
- The GameWorld is filled with Game Entities.
- Entities that have a SoundComponent are able to play sounds.
- These sounds are defined in Acp Files via Sound Nodes.
- Signals are used to interface between the GameWorld and the Audio. They are stored in and accessible from an Entity's SignalsManagerComponent as well as the GameSignalsManager.
- In a similar way as Global Signals, Variables can be used to pass values from the GameWorld to the Audio System and vice versa.
- The GameCode or Scripts can instruct an Entity's SoundComponent to play a Sound with a given Sound Event Name.
- The SoundComponent will then search through its assigned acp files and look for Sound Nodes whose names match the given Sound Event name. If a matching Sound Node was found, it will be processed based on its audio signal chain, taking into account available Signals.
- The sound will be sent to the a submix input of the Mixer (FinalMix) where the submixes are further processed.
- Enfusion's Audio System will handle the main processing of the audio generation.
- The generated audio will be forwarded to the system'S audio API, e.g WASAPI (a Windows audio API), in order to actually play back the sound on the user's system.
Game Entities
The Enfusion Engine uses a modular entity system. An Entity in and on itself is just a set of functionalities defined via GameCode or even a completely "empty shell". It is the modules inside, called "Components", that determine the majority of its characteristics. Therefore, Entities in our GameWorld can be anything - from concrete, complex objects like player characters, weapons and buildings, to abstract systems like an entity that manages the rules of a gamemode.
In order to play a sound, an Entity needs to have a variation of the SoundComponent.
SoundComponents
Acp Project Files
Acp project files
Acp (AudioComponent) files determine how sounds behave ingame. Using the Audio Editor, .acp files allow the creation of complex audio processing chains that result in the final sound audible in-game.
Furthermore, .acp files are a mandatory part of the game's audio pipeline, as they contain the Sound names referenced by the SoundComponent when it is instructed to play a sound.
Sound Nodes
Sound Events
Signals
Sound Events
Variables
Mixer
FAQ
- Do Entities need a SignalsManagerComponent to use Signals?
- Yes and no. Some variations of the SoundComponent set some Signals automatically, like the distance of the Entity to the current listener.
- Using the AddOrFindSignal() method, a Signal can also be set when playing a sound, but it will not be stored due to the lack of a SignalsManagerComponent.
- How are Signals set on an Entity's SignalsManagerComponent?
- Some Signals are set via GameCode and cannot be altered, such as the distance of the Entity to the current listener.
- Signals can also be set via scripting by using the AddOrFindSignal() and AddOrFindMPSignal() methods.