Function: Difference between revisions
m (→Usage) |
m (→Usage) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Functions should be used for any processes where the '''result''' or '''calculation''' done in the function is important. This result or calculation should be made in the '''least time possible'''. They are different to [[Script (File)|scripts]], where ''timing'' is important. | Functions should be used for any processes where the '''result''' or '''calculation''' done in the function is important. This result or calculation should be made in the '''least time possible'''. They are different to [[Script (File)|scripts]], where ''timing'' is important. | ||
Functions can also be used to '''reuse code'''. You can some code | Functions can also be used to '''reuse code'''. You can write some code once in the function and then include it in many different scripts. When the code is updated, it is updated for all scripts. When you only copy and paste the code to the other scripts, you have to update every script on any change. | ||
== Syntax == | == Syntax == | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 22 December 2006
A function is a special kind of a script. The common extension for function files is .sqf.
A function is much like a regular scripting command, except that you can use functions to create something like a custom command. A function does something and can then return a value to the point which 'called' that function or it can simply return Nothing.
Introduction
Functions were first introduced into an Operation Flashpoint: Resistance patch.
Usage
Functions should be used for any processes where the result or calculation done in the function is important. This result or calculation should be made in the least time possible. They are different to scripts, where timing is important.
Functions can also be used to reuse code. You can write some code once in the function and then include it in many different scripts. When the code is updated, it is updated for all scripts. When you only copy and paste the code to the other scripts, you have to update every script on any change.
Syntax
Functions are strictly limited to SQF syntax.
Execution
Functions can be executed from several points in the game:
- Other scripts
- Other functions
- Scripting lines in the Mission Editor
- Event Handlers in addon config files
Functions are first loaded as String from a file via preprocessFile or loadFile. They are then executed via the call command. Since Armed Assault the loaded String needs to be compiled in order to convert it to Code, which is requried for call.
Example (Operation Flashpoint):
myFunction1 = loadFile "myFunction1.sqf"; myFunction2 = preprocessFile "myFunction2.sqf"; call myFunction1; [1, 2] call myFunction2;
Example (Armed Assault):
myFunction1 = compile loadFile "myFunction1.sqf"; myFunction2 = compile preprocessFile "myFunction2.sqf"; call myFunction1; [1, 2] call myFunction2;
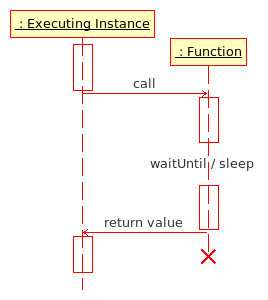
Functions are running within the executing instance, which waits for the result of the function. Different to scripts, functions halt all other game engine processes until the function has completed its instructions. This means functions run faster than scripts, and the result of functions is immediate and unambiguous. It can also mean that if a function takes too long to run it will have an adverse effect on game play - large functions or CPU intensive functions can cause the game to seize up until it completes. When creating a functions you want the function to be short and sweet to achieve the best results.
Note: You can still use the special variables and commands of scripts in functions (Armed Assault only)!
Limitations
Functions have a limitation of 10,000 loops before they are forced to exit by the game engine in order to maintain some level of stability.
Return Value
The last Expression given in a function is returned to the calling instance. Note that there must not be a semicolon after this value.
return.sqf
STATEMENT 1; STATEMENT 2; RETURN_VALUE
test.sqf
value = call compile preprocessFile "return.sqf"; // value is now RETURN_VALUE call compile preprocessFile "return.sqf"; // valid, but RETURN_VALUE is not saved anywhere
Examples
Example 1: max.sqf
In this example the function returns maximum of first and second argument.
max.sqf
comment "Return maximum of first and second argument"; private ["_a","_b"]; _a = _this select 0; _b = _this select 1; if (_a>_b) then {_a} else {_b}
executing script:
fMax = compile preprocessFile "max.sqf"; maxValue = [3,5] call fMax; // maxValue is now 5
Example 2: infantrySafe.sqf
In this example the function returns no value and switches all units to safe mode.
comment "Switch all infantry units to safe mode"; { if (vehicle _x == _x) then { _x setBehaviour "safe" } } forEach _this
Example 3: Inline Function
An inline-function can be created in any script:
FNC_sayhello = {hint format["hello %1",_this]};
This function can then be called (in other scripts, functions, unit's init lines, trigger activation fields, etc.) via:
name player call FNC_sayhello
Notice that there are no brackets around the functions arguments which precede the call command.
In case the function doesn't require any arguments you can just call the function.
call FNC_helloall