Position: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
However, this is incorrect. ATL is a relative format, and while the ATL height between the coordinates is the same, the ASL height might not be (think of the mountain example again). <br> | However, this is incorrect. ATL is a relative format, and while the ATL height between the coordinates is the same, the ASL height might not be (think of the mountain example again). <br> | ||
This is the correct way to write the above code: | This is the correct way to write the above code: | ||
<code>[[private]] _pos1 [[=]] [[getPosASL]] _unit;<br>[[private]] _pos2 [[=]] _pos1 [[vectorAdd]] [0,200,0]; {{cc|make a horizontal line by shifting the y}}<br>[private]] _intersects [[=]] [[lineIntersectsSurfaces]] [_pos1, _pos2]; </code> | <code>[[private]] _pos1 [[=]] [[getPosASL]] _unit;<br>[[private]] _pos2 [[=]] _pos1 [[vectorAdd]] [0,200,0]; {{cc|make a horizontal line by shifting the y}}<br>[[private]] _intersects [[=]] [[lineIntersectsSurfaces]] [_pos1, _pos2]; </code> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 15:23, 10 August 2021
Introduction
Positions in Arma are always represented as arrays. There are two types of positions:
- 2D positions: [X, Y]
- 3D positions: [X, Y, Z]
On the map, the X-axis runs from west to east and the Y-axis runs from south to north. The origin [0, 0] is (usually) located in the bottom left corner.
While the Z-coordinate is always the height, the point relative to which that height is measured depends on the specific position format (see below).
Formats
There are a number of formats available in Real Virtuality:
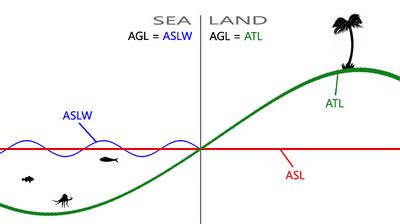
| ASL: | Presumably "Above Sea Level" |
| ATL: | Presumably "Above Terrain Level" |
| ASLW: | Presumably "Above Sea Level including Waves" |
| AGL: | Presumably "Above Generic/Ground Level" |
| AGLS: | Presumably "Above Generic/Ground Level including Surfaces" |
| World: | Raw world coordinate system |
| Relative: | Position relative to an object within its model space |
| Config: | Position used in configs |
| Object: | When object is used for position, PositionWorld of the object is used |
PositionASL
Z is measured from the sea level which is constant across the map.
See also: getPosASL, setPosASL, getPosASLVisual, visiblePositionASL, ASLToATL, ATLToASL, AGLToASL, ASLToAGL, eyePos, aimPos, getTerrainHeightASL, lineIntersects, lineIntersectsWith, lineIntersectsObjs, lineIntersectsSurfaces, terrainIntersectASL, playSound3D, setDefaultCamera
PositionASLW
Z is measured from the surface of the sea that could be higher or lower than sea level due to waves.
See also: getPosASLW, setPosASLW
PositionATL
Z is measured from the terrain level which varies across the map.
See also: getPosATL, setPosATL, getPosATLVisual, ASLToATL, ATLToASL
PositionAGL
Z is the same as in PositionASLW when over sea and is the same as in PositionATL when over land. Most commands either take or return PositionAGL.
See also: modelToWorld, worldToModel, modelToWorldVisual, worldToModelVisual, positionCameraToWorld, intersect, terrainIntersect, isOnRoad, drawIcon3D, drawLine3D, distance, moveTo, doMove, move, setDestination, buildingPos, screenToWorld, worldToScreen, AGLToASL, ASLToAGL, unitAimPosition, unitAimPositionVisual
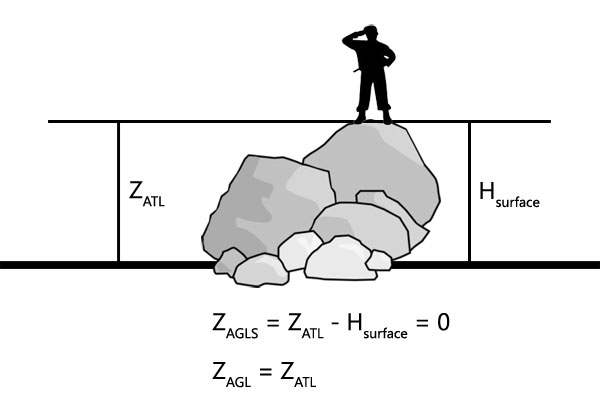
PositionAGLS
Over land, Z is measured as height over terrain level minus the height of surface over terrain level underneath. If such surface exists and is counted in, the resulting Z becomes 0.
Over sea it gets even more complicated as instead of PositionATL, PositionASLW is used minus the offset for the surface height, presumably over waves too, as Z seems static. As there is currently no way to obtain Hsurface, it becomes impossible to convert given PositionAGLS into other formats, unlike with other position formats.
See also: position, visiblePosition, getPos, getPosVisual
setPosAGLS
The function below will place passed object onto walkable surface, if there is one, otherwise on the ground. If only X and Y of the position are supplied, the object will be placed on surface, if Z is supplied, it will be treated as offset from the surface level.
KK_fnc_setPosAGLS = {
params ["_obj", "_pos", "_offset"];
_offset = _pos select 2;
if (isNil "_offset") then {_offset = 0};
_pos set [2, worldSize];
_obj setPosASL _pos;
_pos set [2, vectorMagnitude (_pos vectorDiff getPosVisual _obj) + _offset];
_obj setPosASL _pos;
};
// This will place the player exactly on top deck of Cargo HQ on Stratis:
[player, [2437.18,5693.47,0]] call KK_fnc_setPosAGLS;
// This will place the player 2m above top deck of Cargo HQ on Stratis:
[player, [2437.18,5693.47,2]] call KK_fnc_setPosAGLS;
// This will place the player 2m below top deck of Cargo HQ on Stratis:
[player, [2437.18,5693.47,-2]] call KK_fnc_setPosAGLS;
Alternatively, setVehiclePosition can be used. It will put the object onto the nearest surface.
// This will place the player inside Cargo HQ on Stratis:
player setVehiclePosition [[2437.18,5693.47,0], [], 0, "CAN_COLLIDE"];
// This will place the player on top deck of Cargo HQ on Stratis:
player setVehiclePosition [[2437.18,5693.47,100], [], 0, "CAN_COLLIDE"];
PositionWorld
Similar to PositionASL, however Z is measured from the sea level to the the model centre [0, 0, 0] of the object, rather than transformed boundingCenter or land contact vertices.
_identical = getPosWorld _obj isEqualTo AGLtoASL (_obj modelToWorld [0,0,0]); // should be true
See also: getPosWorld, setPosWorld, mapCenterOnCamera
PositionRelative
Relative position is normally an [X, Y, Z] offset from the model centre.
See also: positionCameraToWorld, selectionPosition, attachTo, modelToWorld, worldToModel, modelToWorldVisual, worldToModelVisual, camPrepareRelPos, camSetRelPos
PositionConfig
The format used in configs, such as mission.sqm, is [X, Z, Y], where Z and Y are swapped around. One other command that uses this format is positionCameraToWorld. Z in configs is measured from the sea level.