Position: Difference between revisions
(minor additions to a note about absolute coords) |
Lou Montana (talk | contribs) m (Fix Wikipedia link) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
While the Z-coordinate is always the height/altitude, the point relative to which that height is measured depends on the specific position format (see {{Link|#Types}} below). | While the Z-coordinate is always the height/altitude, the point relative to which that height is measured depends on the specific position format (see {{Link|#Types}} below). | ||
{{Feature|arma3|Since {{arma3}} v1.94: X, Y and Z are limited to values between -50km and +500km. Using any '''setPos*''' command with values greater than that will {{ | {{Feature|arma3|Since {{arma3}} v1.94: X, Y and Z are limited to values between -50km and +500km. Using any '''setPos*''' command with values greater than that will {{Link|https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clamping_(graphics)|clamp}} the value to within these boundaries, not throwing any errors. e.g: | ||
<sqf>player setPosASL [-50001, 500001, 500001]; // player will be set to [-50000, 500000, 500000]</sqf>}} | <sqf>player setPosASL [-50001, 500001, 500001]; // player will be set to [-50000, 500000, 500000]</sqf>}} | ||
Revision as of 01:04, 24 February 2023
Positions in Arma games are always represented as arrays. There are two types of positions:
- 2D position: [X, Y]
- 3D position: [X, Y, Z]
On the map and on the terrain, the X-axis runs from west to east and the Y-axis runs from south to north. The origin [0, 0] is (usually) located in the bottom left corner.
While the Z-coordinate is always the height/altitude, the point relative to which that height is measured depends on the specific position format (see Types below).
Commands
See:
Types
There are a number of formats available in Real Virtuality:
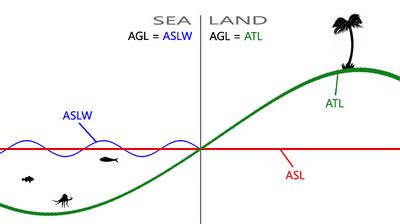
| ASL: | Presumably "Above Sea Level" |
| ATL: | Presumably "Above Terrain Level" |
| ASLW: | Presumably "Above Sea Level including Waves" |
| AGL: | Presumably "Above Generic/Ground Level" |
| AGLS: | Presumably "Above Generic/Ground Level including Surfaces" |
| World: | Raw world coordinate system |
| Relative: | Position relative to an object within its model space |
| Config: | Position used in configs |
| Object: | When object is used for position, PositionWorld of the object is used |
| Visual: | Used for rendering objects on the screen. Useful for per-frame applications, such as drawIcon3D - see Command Group: Render Time Scope and Simulation vs Render Time Scope. |
Position2D
This array only has two elements and is usually used with 2D information, for example standard markers or UI commands. If used with e.g distance, Z is assumed to be 0.
PositionASL
Z is measured from the sea level which is constant across the map.
See also: getPosASL, setPosASL, getPosASLVisual, visiblePositionASL, ASLToATL, ATLToASL, AGLToASL, ASLToAGL, eyePos, aimPos, getTerrainHeightASL, lineIntersects, lineIntersectsWith, lineIntersectsObjs, lineIntersectsSurfaces, terrainIntersectASL, playSound3D, setDefaultCamera
PositionASLW
Z is measured from the surface of water at that position. Both waves and pond objects affect the result.
See also: getPosASLW, setPosASLW
PositionATL
Z is measured from the terrain level which varies across the map.
See also: getPosATL, setPosATL, getPosATLVisual, ASLToATL, ATLToASL
PositionAGL
Z is the same as in PositionASLW when over sea and is the same as in PositionATL when over land. Most commands either take or return PositionAGL.
See also: modelToWorld, worldToModel, modelToWorldVisual, worldToModelVisual, positionCameraToWorld, intersect, terrainIntersect, isOnRoad, drawIcon3D, drawLine3D, distance, moveTo, doMove, move, setDestination, buildingPos, screenToWorld, worldToScreen, AGLToASL, ASLToAGL, unitAimPosition, unitAimPositionVisual
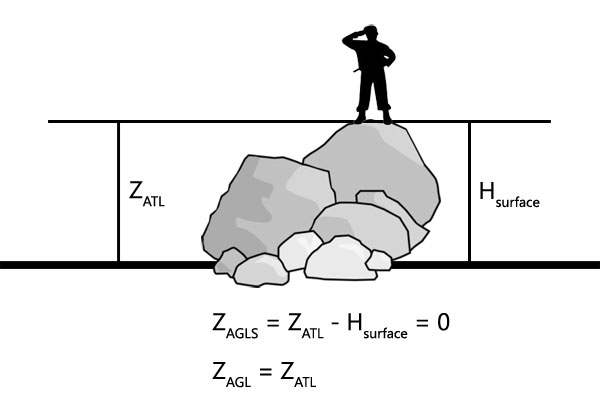
PositionAGLS
Over land, Z is measured as height over terrain level minus the height of surface over terrain level underneath. If such surface exists and is counted in, the resulting Z becomes 0.
Over sea it gets even more complicated as instead of PositionATL, PositionASLW is used minus the offset for the surface height, presumably over waves too, as Z seems static. As there is currently no way to obtain Hsurface, it becomes impossible to convert given PositionAGLS into other formats, unlike with other position formats.
See also: position, visiblePosition, getPos, getPosVisual
setPosAGLS
The function below will place passed object onto walkable surface, if there is one, otherwise on the ground. If only X and Y of the position are supplied, the object will be placed on surface, if Z is supplied, it will be treated as offset from the surface level.
Alternatively, setVehiclePosition can be used. It will put the object onto the nearest surface.
PositionWorld
Similar to PositionASL, however Z is measured from the sea level to the the model centre [0, 0, 0] of the object, rather than transformed boundingCenter or land contact vertices.
See also: getPosWorld, setPosWorld, mapCenterOnCamera
PositionRelative
Relative position is normally an [X, Y, Z] offset from the model centre.
See also: positionCameraToWorld, selectionPosition, attachTo, modelToWorld, worldToModel, modelToWorldVisual, worldToModelVisual, camPrepareRelPos, camSetRelPos
PositionConfig
The format used in configs, such as mission.sqm, is [X, Z, Y], where Z and Y are swapped around. One other command that uses this format is positionCameraToWorld. Z in configs is measured from the sea level.